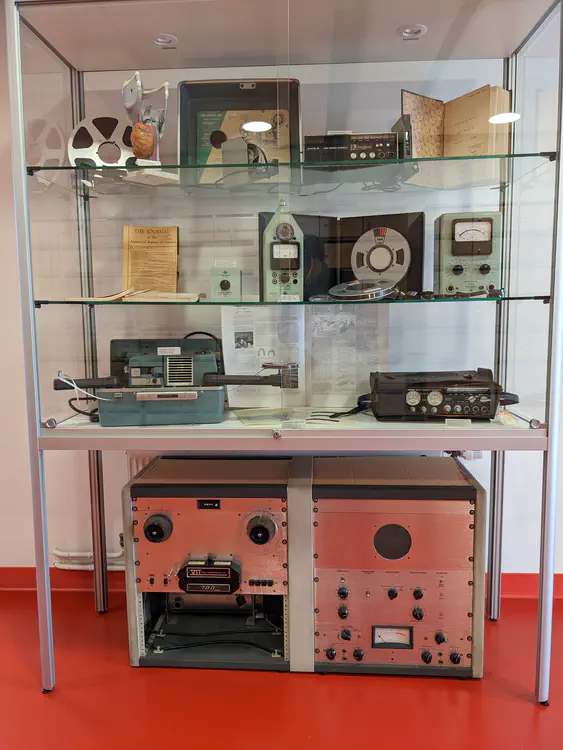
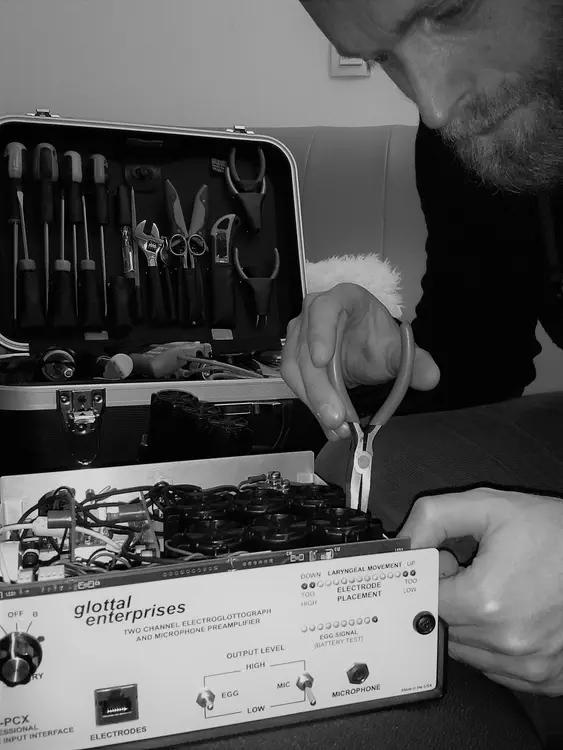
Emmanuel Ferragne
Professor of Phonetics
Deputy head of ALTAE
Works at Université Paris Cité
Institut Universitaire de France (IUF)
inIdEx Empirical Foundations of Linguistics (EFL)
About me
I am a full professor of phonetics in the English Studies department at Université Paris Cité.
- Sociophonetics/Neurophonetics
- Forensic phonetics
- Learners’ pronunciation
Featured Publications
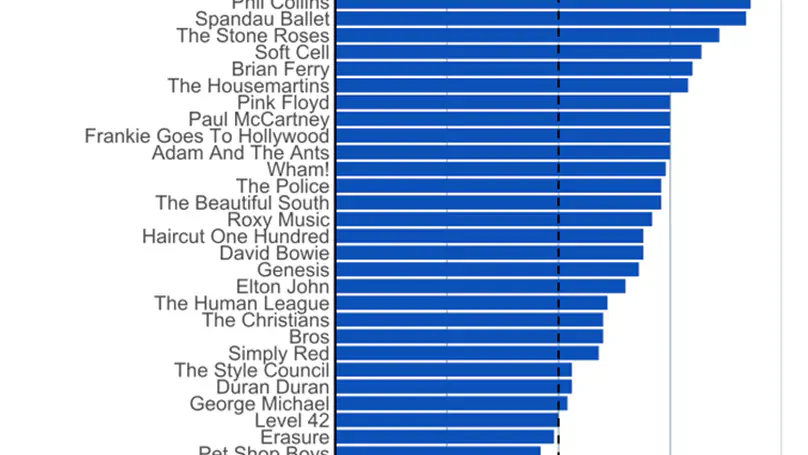
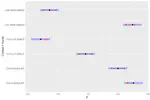
A quantitative study of word internal intervocalic /t/ pronunciation as a marker of an American accent (where a flapped alveolar realization is considered typically American as opposed to a more characteristically British alveolar stop) was carried out on a database of 350 randomly sampled songs from top 10 albums for each year of the decade.
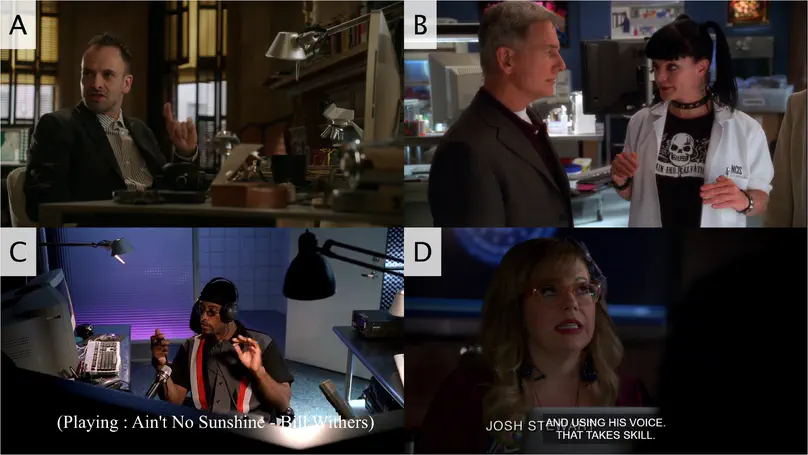

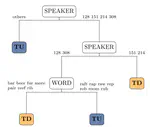
People’s perception of forensic evidence is greatly influenced by crime TV series. The analysis of the human voice is no exception. However, unlike fingerprints—with which fiction and popular beliefs draw an incorrect parallel—the human voice varies according to many factors, can be altered deliberately, and its potential uniqueness has yet to be proven. Starting with a cursory examination of landmarks in forensic voice analysis that exemplify how the voiceprint fallacy came about and why people think they can recognize people’s voices, we then provide a thorough inspection of over 100 excerpts from TV series. Through this analysis, we seek to characterize the narrative and aesthetic processes that fashion our perception of scientific evidence when it comes to identifying somebody based on voice analysis. These processes converge to exaggerate the reliability of forensic voice analysis. We complement our examination with plausibility ratings of a subset of excerpts. We claim that these biased representations have led to a situation where, even today, one of the main challenges faced by forensic voice specialists is to convince trial jurors, judges, lawyers, and police officers that forensic voice comparison can by no means give the sort of straightforward answers that fingerprints or DNA permit.
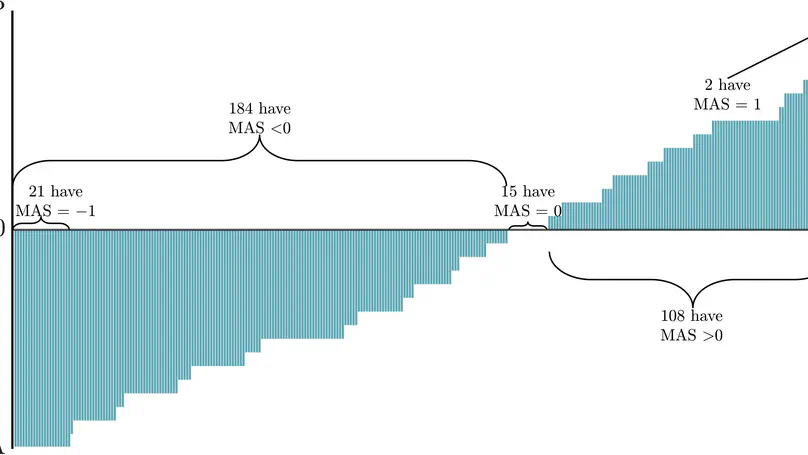
Acquiring a consistent accent and targeting a native-standard-like Received Pronunciation (RP) or General American (GA) are prerequisites for French learners who plan to become English teachers in France. Reliable methods to assess learners’ productions are therefore extremely valuable. We recorded a little over 300 students from our English Studies department and performed auditory analysis to investigate their accents and determine how close to native models their productions were. Inter-rater comparisons were carried out; they revealed overall good agreement scores which, however, varied across phonetic cues. Then, automatic speech recognition (ASR) and automatic accent identification (AID) were applied to the data. We provide exploratory interpretations of the ASR outputs, and show to what extent they agree with and complement our auditory ratings. AID turns out to be very consistent with our perception, and both types of measurements show that two thirds of our students favour an American, and the remaining third, a British pronunciation, although most of them have mixed features from the two accents.
Recent Publications
Projects
Praat and R code for a doctoral seminar I teach at Université Paris Diderot.speech corpora.


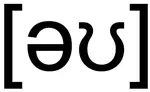

![[ɹ], [w] or [ʁ]: Investigating French advanced learners' productions of English /r/](/talk/%C9%B9-w-or-%CA%81-investigating-french-advanced-learners-productions-of-english-/r/featured_huf04e41ab7ab5b8c501a055280a804cf2_38383_150x0_resize_q75_h2_lanczos.webp)